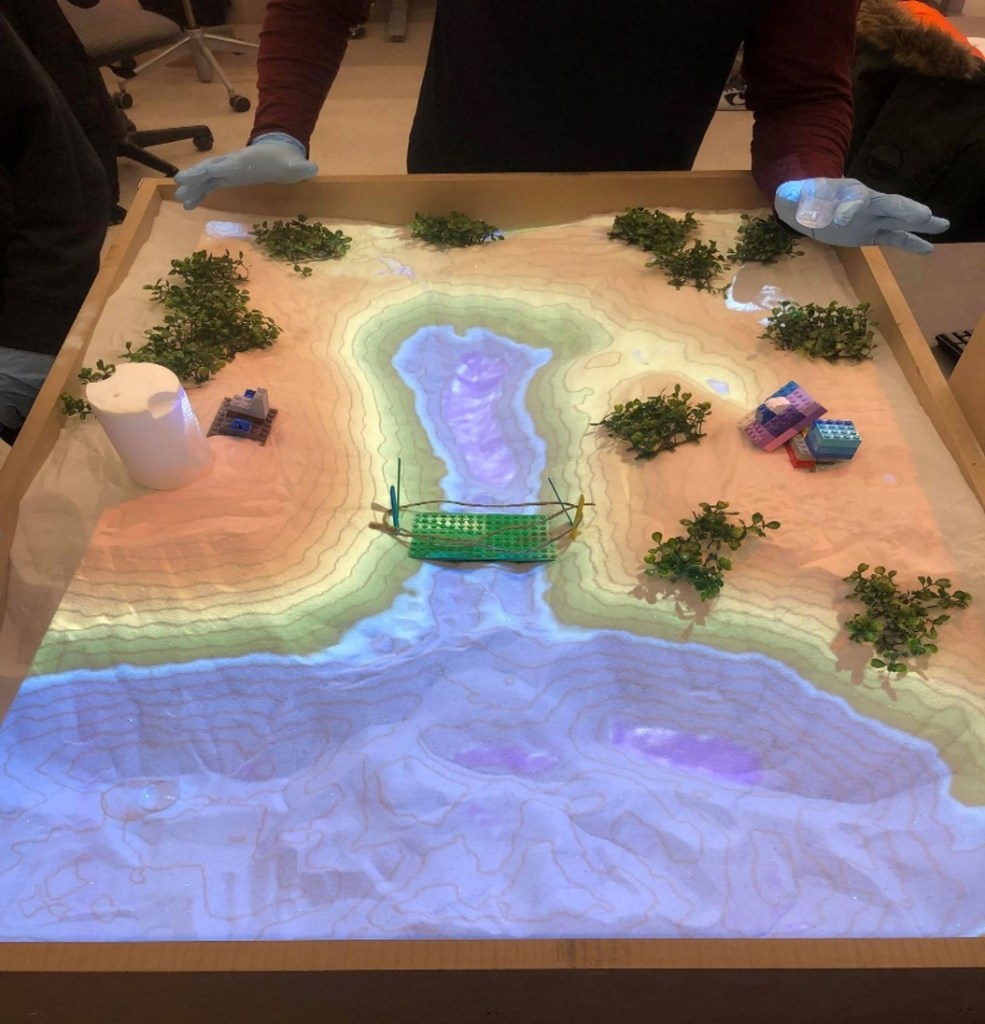

A New Realm of Experiential Education Using an Augmented Reality Sandbox
Project Leads: Majgan Jadidi, Matthew Perras, Usman Khan, Melanie Baljko
Augmented Reality (AR) technology expands the physical world by adding digital information layers onto what we can see with the naked eye. The virtual layers (topography, geology, hydrogeology, and other Earth-related elements) help students engage with the visualization of 3D problems, something that traditional 2D class material does not readily afford. AR is beginning developed for use in education and students from the technology-infused generation are very familiar and comfortable with these technologies. Therefore, AR technology provides an experiential environment that students intuitively utilize and will allow them to experience the physical environment where fieldwork is inaccessible or expensive. The main goal is to embed such technologies and enhance our students’ experiential education from first through to fourth-year courses across Lassonde School of Engineering. This will spark student curiosity, improving their visual understanding, going beyond the classroom to see and experience the impact of their decisions on the design in an immersed environment.

Low Impact Development (LlD), Optimized and cost-effective LID types
Sarah Kaykhosravi, PhD Candidate
The primary goal of low impact development (LID) is to capture urban stormwater runoff; however, multiple indirect benefits (environmental and socioeconomic benefits) also exist (e.g., improvements to human health and decreased air pollution). Identifying sites with the highest demand or need for LID ensures the maximization of all benefits. This is a spatial decision-making problem that has not been widely addressed in the literature and was the focus of this research.
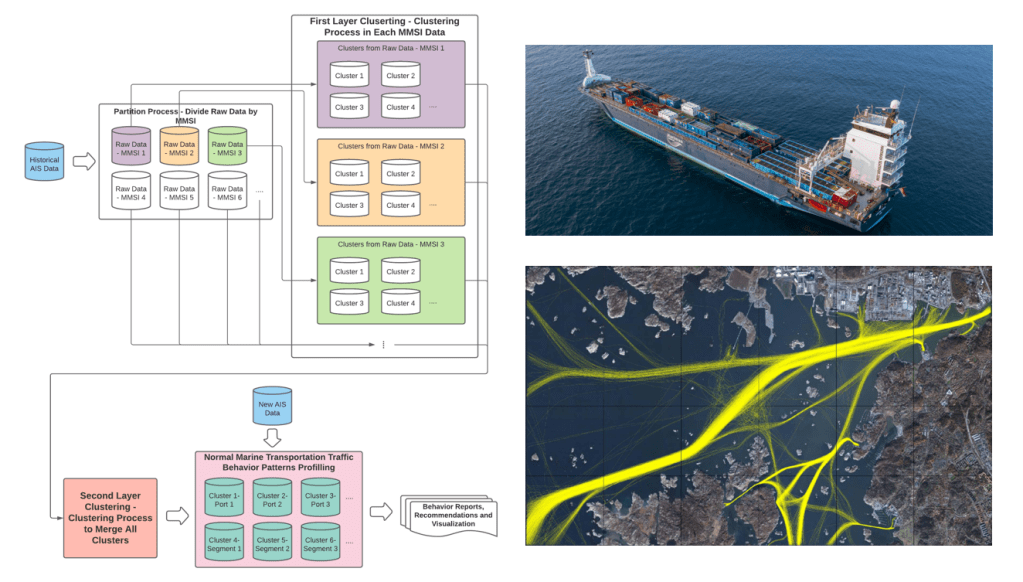
Modelling Vessel Behaviours by Clustering Marine Automatic Identification System (AIS) Data Using Optimized DBSCAN
Xuyang Han, Master of Science
Today, maritime transportation represents substantial international trade. Sustainable development of marine transportation requires systematic modeling and surveillance for maritime situational awareness. In this research, we present an enhanced density-based spatial clustering (DBSCAN) method to model vessel behaviors. The proposed methodology enhances the DBSCAN clustering performance by integrating the Mahalanobis Distance metric that considers the correlations of the points representing the locations of the vessels. The clustering method is applied to historical Automatic Identification System (AIS) data and generates an action recommendation tool and a model for detecting vessel trajectory anomalies.

Quantum Computing
Amirhossein Nourbakhsh, PhD Candidate
Quantum computing is the use of quantum phenomena such as superposition and entanglement to perform computation. Computers that perform quantum computations are known as quantum computers. They are believed to be able to solve certain computational problems, such as integer factorization, substantially faster than classical computers.

Knowledge Discovery in 3DCity Model and BIM (Geo-BIM)
Hamid Kiavarz, PhD Candidate
Urban and population growth results in increasing pressure on the public utilities like transport, energy, healthcare services, crime management and emergency services in the realm of smart city management. The smart management and decision making obliges the urban management to use 3D data rather 2D information to solve the complex problems.
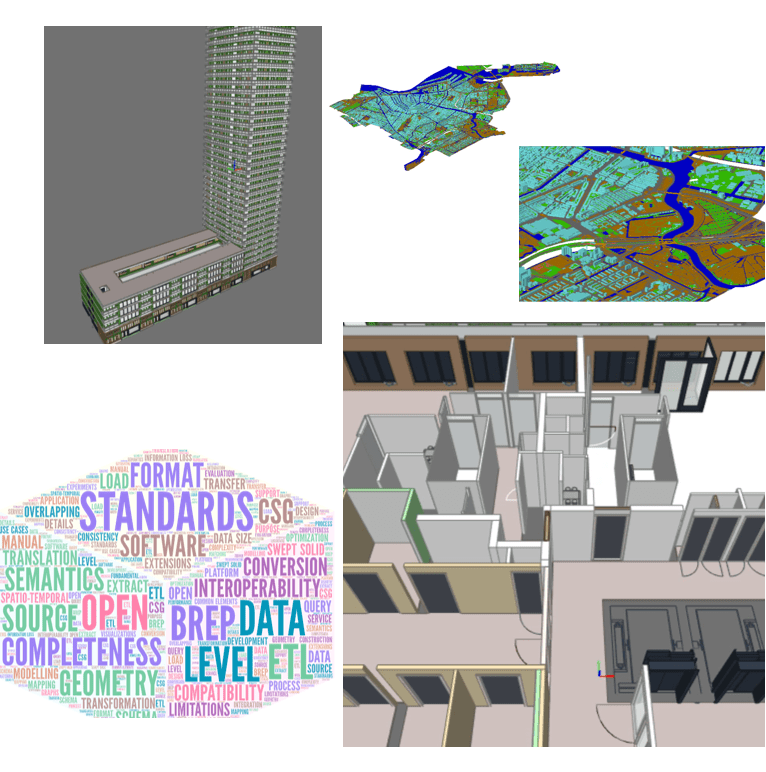
Towards the Interoperability of BIM and GIS using Semantic Web Technology
Aman U. Usmani, Master Candidate
- BIM and GIS are distinct domains with detailed semantic data models.
- Integration of these fundamentally heterogenous systems crucial for urban planning and management, especially Smart Cities.
- Problematic data models and inadequate integration solutions.
- How about turning to Smart Data?
- Applying Semantic Web Technologies to bring BIM and GIS data in Smart Data format
- For linking and annotation Semantic Web has RDF at its core, but in order to create inference and reasoning, Semantic Web utilizes Ontology (OWL)
- Focus: automatic ontology development for semantic data of BIM and GIS

How can Cycling be Made Safer?
Htoo Win Aung, Undergraduate Student
An analysis of cyclist safety in Toronto and its primary influential factors, using a mix of literature review and geospatial data mapping. The main goal of the project is to determine the key parameters of cyclist safety and what can be done to improve on each of them. Certain accident hotspots in Toronto are used as case studies, using publicly available datasets collected by reputable sources, as a form of real-world application.